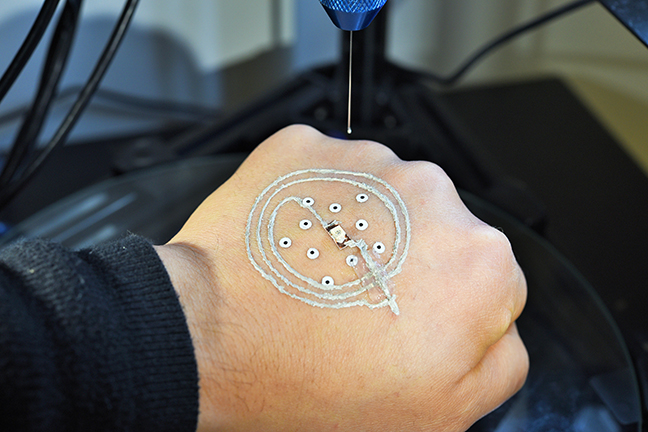
In a groundbreaking new study, researchers at the University of Minnesota used a customized, low-cost 3D printer to print electronics on a real hand for the first time. The technology could be used by soldiers on the battlefield to print temporary sensors on their bodies to detect chemical or biological agents or solar cells to charge essential electronics.
Researchers also successfully printed biological cells on the skin wound of a mouse. The technique could lead to new medical treatments for wound healing and direct printing of grafts for skin disorders.
The research study was published today on the inside back cover of the academic journal Advanced Materials.
“We are excited about the potential of this new 3D-printing technology using a portable, lightweight printer costing less than $400,” said Michael McAlpine, the study’s lead author and the University of Minnesota Benjamin Mayhugh Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering. “We imagine that a soldier could pull this printer out of a backpack and print a chemical sensor or other electronics they need, directly on the skin. It would be like a ‘Swiss Army knife’ of the future with everything they need all in one portable 3D printing tool.”
One of the key innovations of the new 3D-printing technique is that this printer can adjust to small movements of the body during printing. Temporary markers are placed on the skin and the skin is scanned. The printer uses computer vision to adjust to movements in real-time.
“No matter how hard anyone would try to stay still when using the printer on the skin, a person moves slightly and every hand is different,” McAlpine said. “This printer can track the hand using the markers and adjust in real-time to the movements and contours of the hand, so printing of the electronics keeps its circuit shape.”
Another unique feature of this 3D-printing technique is that it uses a specialized ink made of silver flakes that can cure and conduct at room temperature. This is different from other 3D-printing inks that need to cure at high temperatures (up to 100 degrees Celsius or 212 degrees Fahrenheit) and would burn the hand.
To remove the electronics, the person can simply peel off the electronic device with tweezers or wash it off with water.
In addition to electronics, the new 3D-printing technique paves the way for many other applications, including printing cells to help those with skin diseases. McAlpine’s team partnered with University of Minnesota Department of Pediatrics doctor and medical school Dean Jakub Tolar, a world-renowned expert on treating rare skin disease. The team successfully used a bioink to print cells on a mouse skin wound, which could lead to advanced medical treatments for those with skin diseases.
“I’m fascinated by the idea of printing electronics or cells directly on the skin,” McAlpine said. “It is such a simple idea and has unlimited potential for important applications in the future.”
In addition to McAlpine and Tolar, the University of Minnesota team includes Ph.D. students Zhijie Zhu and Xiaoxiao Fan and postdoctoral researcher Shuang-Zhuang Guo from the Department of Mechanical Engineering in the College of Science and Engineering; and research staff Cindy Eide and Tessa Hirdler from the Department of Pediatrics in the Medical School.
This study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and state-funded Regenerative Medicine Minnesota. In addition, the first author of the paper Zhijie Zhu was funded by a University of Minnesota Interdisciplinary Doctoral Fellowship.
To read the full research paper entitled “3D Printed Functional and Biological Materials on Moving Freeform Surfaces,” visit the Advanced Materials website.