Introduction
The MC27561-DRAGONFLY is part of Arrow’s board family called SmartEverything. This board is a ready-to-use Internet of Things (IoT) hardware. It is Arduino IDE compatible which allows fast and easy software development. Any kind of Arduino form factor connectors can be added on top if necessary.
The board’s main features are the following:
- Microchip MCU for Arduino compatibility
- Dusty module from IOTeam, performing SmartMesh IP® operations
- A SigFox module from IOTeam for low power, long range wireless communication
- A Wi-Fi module from Microchip
The above mentioned modules make the DRAGONFLY an ideal triple-play gateway solution.
SmartMesh IP®
Probably this technology is the most unfamiliar to most readers. In the followings You will learn about its terminology and the basics of operation.
SmartMesh IP® combines reliability and ultra low-power with a native Internet Protocol (IP) layer for a robust, standards-based offering perfect for a broad range of applications. SmartMesh IP® provides robust wire-free connectivity for applications where low power, reliability, and ease of deployment matter. Every node in a SmartMesh IP® network can run on batteries for years, or virtually forever with an energy harvesting power source. The ability to put a sensor anywhere, without wiring, allows network deployments that do not disrupt building operations or occupants. With built-in intelligence that enables the mesh network to self-form and self-maintain, SmartMesh IP® systems are easily deployed by field technicians with no wireless technology expertise.
A SmartMesh IP® network consists of the following:
- SmartMesh IP® manager
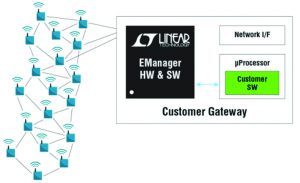
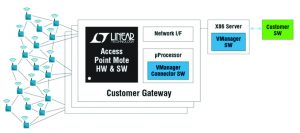
SmartMesh IP® network managers perform two major functions for the mesh network. First they serve as an access point mote, connecting the wireless mesh to customer host applications. Second, network managers run sophisticated network management algorithms to maintain performance of the network.
Two manager options are available:
- an embedded version (EManager) used for small (less than 100 devices) networks with an integrated Access
- Point Mote (APM)
Figure 1 – EManager
- a larger server-class version called VManager for larger installations, and can be used with multiple Access Point Motes.
Figure 2 – VManager
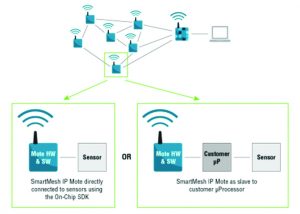
- SmartMesh IP® motes
SmartMesh IP® Motes are the wireless nodes in a SmartMesh IP® network. They connect to sensors/actuators and route data from other motes, yet remain low power.
Each mote can both send and receive messages (supports bidirectional data). Each mote may have a different data reporting rate and the network manager will automatically coordinate individual pair-wise communications to efficiently route the traffic.
Each mote may have a different power supply capability (e.g. line-, battery-, or energy- harvested power). The network manager will load balance traffic accordingly to extend time until the network’s first battery replacement.
- default factory firmware mote in master mode (no external API client required)
- default factory firmware mote in slave mode attached to an API client such as a microcontroller.
Figure 3 – Motes
SmartMesh IP features
- Ultra low-power network – The network can run on batteries, energy harvesting, or line power
- High network reliability – >99.999% network reliability even in harsh RF environments
- IPv6 addressability – Combines 6LoWPAN with IEEE 802.15.4e
- Comprehensive security management – Allows you to configure NIST-certified AES-128 based security to meet your requirements
- Flexible configuration – Network parameters can be selected to match specific system requirements (power / latency / bandwidth)
- Fully tested network stack and manager software – Application programming interfaces are used to communicate with and configuring the product – no user networking code necessary.
Network overview
A SmartMesh IP® network consists of a self-forming multi-hop mesh of nodes known as motes, and an Access Point mote that connects the motes to the Network Manager that monitors and manages network performance and security, and acts as a bridge between the host application and the wireless network. Motes are capable of two way communication and collect and relay data. SmartMesh networks communicate using a Time Slotted Channel Hopping (TSCH) link layer, pioneered by Linear’s Dust Networks group. In a TSCH network, all motes are precisely synchronized to within tens of microseconds. Time in the network is organized into timeslots, which enables collision-free packet exchange and per-transmission channel-hopping. In a SmartMesh network, every device has one or more parents (e.g. mote 3 has motes 1 and 2 as parents) that provide redundant paths to overcome communications interruption due to interference, physical obstruction or multi-path fading. If a packet transmission fails on one path, the next re-transmission may try on a different path and different RF channel.